What's the Real Difference between CNC Drilling Machine and CNC Machining Center on Drilling?
Need to drill lots of precise holes, maybe achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches? You might wonder if a dedicated CNC drilling machine, specialized for this task, is the right choice, or if the versatility of a full CNC machining center is necessary. Choosing incorrectly could mean overspending on unused capabilities or lacking the focused precision your parts demand.
A CNC drilling machine is highly specialized for creating accurate holes, usually moving the drill in one direction. A CNC machining center is multifunctional, capable of drilling, milling, tapping, and boring, often with multi-axis tool movement for complex shapes.
So, while both use CNC technology to make holes, their core design philosophies differ significantly. The drilling machine excels at dedicated hole-making with potentially higher specific precision for that task, while the machining center offers broad capabilities. Let’s explore the specific types of drilling machines first.
What Are the Different Types of CNC Drilling Machines?
Heard "CNC drilling machine" but encountered terms like radial arm, gantry, or even turret type? The variety can be confusing, and picking the wrong configuration could limit your part size, complexity, or production efficiency. Understanding the main types helps match the machine structure to your specific drilling needs.
CNC drilling machines come in diverse configurations, including upright, radial arm, gang, multiple spindle, micro-drill, and turret types, each optimized for different workpiece sizes, production volumes, and operational requirements.
At J&M Machine Tools, we recognize that one size doesn’t fit all. Your latest research highlights these key types:
- Upright Drill Press: Often geared, suitable for heavy/large parts where the operator might feed the workpiece. A robust, traditional design adapted for CNC.
- Radial Arm Drill Press: Features a spindle head that moves along an adjustable arm. This allows drilling over a large area on stationary, often bulky, workpieces without repositioning them frequently. Offers great flexibility.
- Gang Drilling Machine: Incorporates multiple drill heads positioned over a single worktable. This allows performing several drilling operations simultaneously or sequentially on a workpiece without moving it between stations, boosting throughput.
- Multiple Spindle Drilling Machine1: Has several spindles driven by a single head, all feeding simultaneously. Excellent for parts requiring many holes in a specific pattern, common in high-volume production.
- Micro Drill Press2: Designed for extremely high accuracy on very small components. Features small chucks and precise controls, essential for industries like electronics or medical devices.
- Turret Type Drilling Machine: Equipped with multiple tools (drills, taps, reamers) mounted on a rotating turret. The turret indexes quickly to bring the required tool into position, minimizing tool change time for sequential operations.
The choice depends heavily on factors like part size (micro vs. large radial arm work), required accuracy (micro drill), number of holes per part (multiple spindle), and the need for sequential operations (turret type).
What Are the Different Types of CNC Drill Bits?
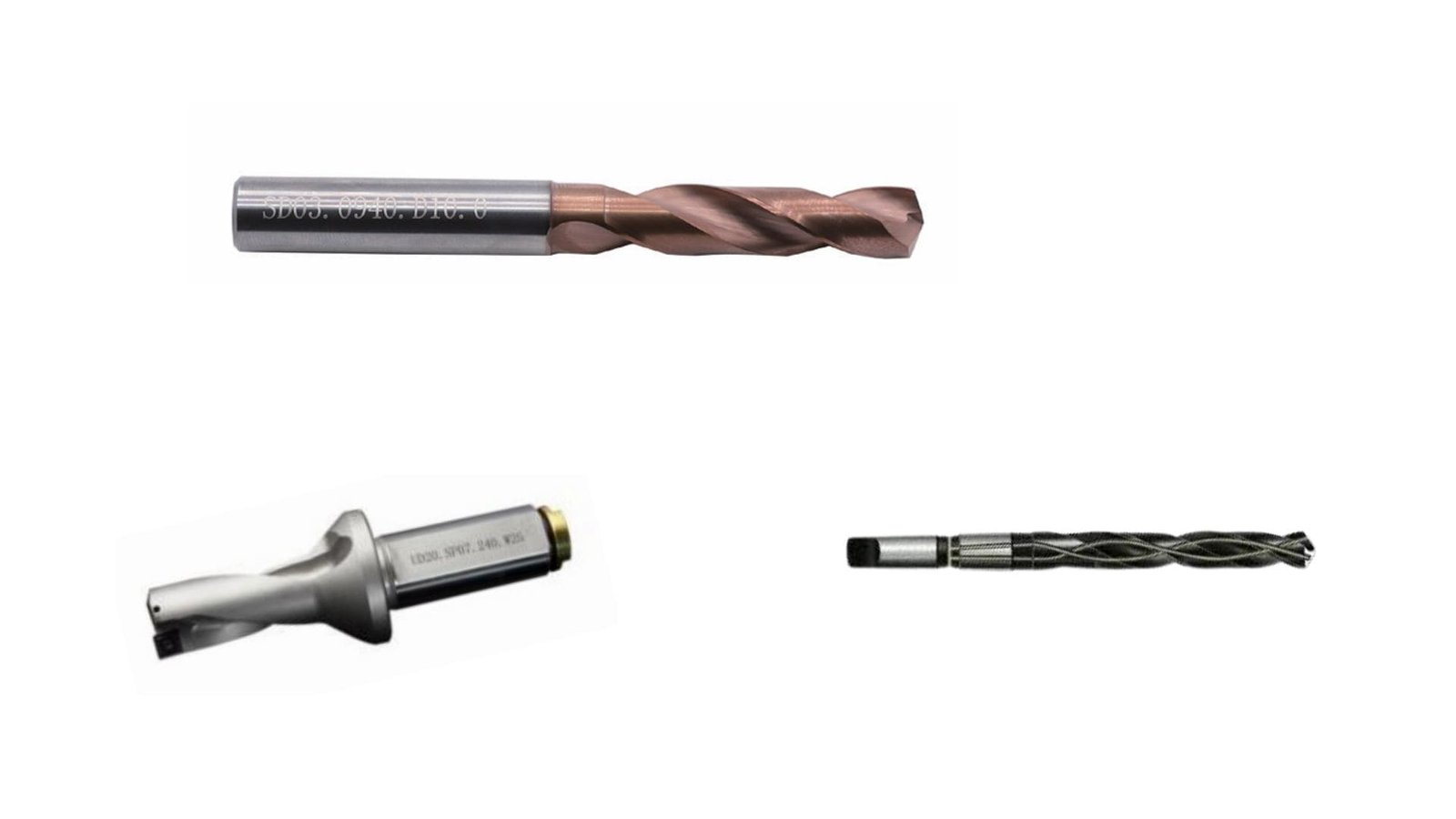
Are you defaulting to standard HSS twist drills for all your CNC hole-making? Using a non-optimal drill bit can lead to poor hole quality (size, straightness, finish), slow cycle times, inaccurate starting positions, or frequent tool breakage, especially in challenging materials or deep holes. Expanding your knowledge of available drill types is key to optimization.
Beyond standard twist drills, CNC drilling utilizes specialized bits like carbide-tipped (hard materials), brad point (wood), step drills (sheet metal), center drills (spotting), oil-hole drills (cooling), deep-hole drills, and combination tools.
Selecting the perfect tool for the job is critical for performance and cost-effectiveness in CNC. Your updated insights cover a broad range:
| Drill Bit Type | Main Purpose | Key Feature(s) / Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Twist Drill | General-purpose drilling. | Most common; HSS or Carbide; Various coatings3 (TiN, etc.). |
| Carbide-Tipped/Solid4 | Drilling hard/abrasive materials at high speeds. | High wear resistance; Stainless steel, cast iron, composites. |
| Brad Point Bit | Precise positioning in wood; prevents wandering. | Sharp center point and spurs; Wood, some plastics. |
| Step Drill Bit | Creates multiple hole sizes in thin material without changing bits. | Conical shape with multiple steps; Sheet metal. |
| Center Drill | Creates an accurate starting spot (center) for larger drills. | Short, rigid; Ensures positional accuracy. |
| Oil Hole Drill | Improves cooling & chip evacuation, especially in deep holes. | Internal coolant channels through the body. |
| Deep Hole Drill | Drilling holes with high depth-to-diameter ratios (e.g., gun drill). | Specialized geometries for chip removal and straightness. |
| Combination Tools | Combines operations (e.g., drill/ream, drill/tap). | Saves tool changes in mass production. |
| Profile Drills | Creates specific forms (e.g., countersink, counterbore, taper). | Shaped tip for chamfers, bolt heads, conical seats. |
Furthermore, consider coatings (like TiN for hardness, TiCN for wear resistance, TiAlN for high heat) and flute design (parabolic for deep holes, straight for brittle materials) as they significantly impact performance and tool life in specific applications.
What Are Important Considerations for Effective CNC Drilling?
Experiencing issues like inconsistent hole quality, rapid tool wear, frequent drill breakage, or slow production times in your CNC drilling operations? Overlooking key process variables is often the root cause, leading to wasted materials, high tooling costs, and inefficient machine usage. Mastering these factors is essential for reliable, high-quality results.
Effective CNC drilling hinges on selecting appropriate materials, choosing the right drill bit (type, material, geometry, coating), optimizing speeds and feeds, utilizing proper coolant, ensuring rigid workpiece fixturing, managing chip evacuation, monitoring tool wear, and employing precise CNC programming.
Achieving consistent, high-quality holes efficiently requires a holistic approach. Your research underscores these vital considerations:
- Material Selection & Compatibility5: Understand the properties (hardness, machinability) of the workpiece material (metals like steel/aluminum, non-metals like plastic/wood, composites like carbon fiber). This dictates tool choice and parameters.
- Optimal Tool Selection: Match the drill bit type, material (HSS, Carbide), diameter, length, point angle, flute design, and coating specifically to the application and workpiece material.
- Speeds and Feeds Optimization6: Carefully balance spindle speed (RPM) and feed rate (mm/min or inch/min) to maximize efficiency without compromising accuracy, finish, or tool life. Start with recommendations, then fine-tune.
- Coolant/Lubricant Strategy: Essential for reducing heat, friction, and wear, especially at high speeds or in tough materials. Choose the right type (oil, synthetic, semi-synthetic) and delivery method (flood, mist, through-spindle).
- Rigid Workholding (Fixturing): The workpiece must be clamped securely to prevent any movement during drilling. Poor fixturing leads to inaccuracy, vibration, and tool breakage.
- Effective Chip Removal7: Chips must be evacuated efficiently from the hole to prevent packing, tool breakage, and poor surface finish. This is critical in deep holes (consider peck drilling cycles or through-spindle coolant).
- Tool Design & Wear Monitoring: Regularly inspect drills for wear or damage. Implement tool life management strategies to replace tools proactively, avoiding unexpected failures and ensuring consistent quality. Consider the drill’s length-to-diameter ratio for rigidity.
- Precise Programming: Utilize CAM software and appropriate G-codes (e.g., G81 drilling cycle, G83 peck drilling cycle) to generate accurate and efficient toolpaths, controlling depths, retracts, and cycles effectively.
Mastering these elements turns CNC drilling into a predictable, precise, and productive process.
Which Industries Rely Heavily on CNC Drilling Machines?
Curious about where CNC drilling technology makes the biggest impact across the manufacturing sector? Identifying the primary user industries highlights the specific strengths of CNC drilling – precision, speed, and repeatability – and might suggest applications relevant to your own field.
CNC drilling is indispensable in industries demanding high volumes of accurate holes, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, industrial equipment, energy, mold making, shipbuilding, and consumer products.
These machines are workhorses where hole-making is a frequent and critical operation. Your comprehensive survey shows widespread use:
- Automotive: Engine blocks, cylinder heads, suspension components, wheel hubs – requiring thousands of precise holes.
- Aerospace: Fuselage panels, wing structures, engine components – demanding extreme accuracy and reliability, often in challenging materials.
- Electronics: Housings, enclosures, connector ports, PCB mounting holes – needing small, precise features.
- Medical Devices: Prosthetics, surgical instruments, dental implants – requiring biocompatible materials8 and high precision.
- Industrial Equipment: Machine frames, flanges, hydraulic components – often involving large parts and robust drilling needs.
- Energy: Turbine components, pipeline flanges, parts for oil & gas extraction – demanding reliability in harsh environments.
- Mold & Die Making: Cooling lines, ejector pins, assembly holes – critical for mold function and accuracy.
- Shipbuilding: Large structural plates, beams – requiring numerous bolt holes, often handled by gantry drills.
- Consumer Products: Appliances, smartphone casings, furniture components – balancing cost, speed, and quality.
- Emerging Tech: Automation, Communication, Robotics, Semiconductors – leveraging precision for innovative components.
The common thread is the need for accurate, repeatable, and often efficient hole production, making CNC drilling a cornerstone technology across diverse manufacturing fields.
Conclusion
Dedicated CNC drilling machines offer specialized precision and efficiency for hole-making tasks, while versatile CNC machining centers handle drilling alongside milling and other operations. Choose based on your primary need: focused, high-precision drilling or broader machining capabilities.
-
Learn how Multiple Spindle Drilling Machines can enhance throughput in high-volume production settings. ↩
-
Discover the critical role of Micro Drill Presses in precision industries like electronics and medical devices. ↩
-
Learn about various drill bit coatings and their impact on performance, tool life, and application suitability for your projects. ↩
-
Discover why Carbide-Tipped/Solid drill bits are essential for drilling hard materials at high speeds, ensuring durability and precision. ↩
-
Understanding material properties is crucial for effective machining. Explore this link to enhance your knowledge on material selection. ↩
-
Optimizing speeds and feeds is key to maximizing efficiency and tool life. Discover expert tips and techniques to improve your CNC operations. ↩
-
Efficient chip removal is vital for maintaining tool performance and surface finish. Learn about the best practices to enhance your drilling process. ↩
-
Learn about the importance of biocompatible materials in medical devices and their role in patient safety and device performance. ↩

Chris Lu
Leveraging over a decade of hands-on experience in the machine tool industry, particularly with CNC machines, I'm here to help. Whether you have questions sparked by this post, need guidance on selecting the right equipment (CNC or conventional), are exploring custom machine solutions, or are ready to discuss a purchase, don't hesitate to CONTACT Me. Let's find the perfect machine tool for your needs.