What are the 5 axis on a CNC Machining Center?

Chris Lu
Leveraging over a decade of hands-on experience in the machine tool industry, particularly with CNC machines, I'm here to help. Whether you have questions sparked by this post, need guidance on selecting the right equipment (CNC or conventional), are exploring custom machine solutions, or are ready to discuss a purchase, don't hesitate to CONTACT Me. Let's find the perfect machine tool for your needs.

Chris Lu
Leveraging over a decade of hands-on experience in the machine tool industry, particularly with CNC machines, I'm here to help. Whether you have questions sparked by this post, need guidance on selecting the right equipment (CNC or conventional), are exploring custom machine solutions, or are ready to discuss a purchase, don't hesitate to CONTACT Me. Let's find the perfect machine tool for your needs
You keep hearing about "5-axis" CNC machines, but what does that actually mean? It sounds complicated, and the terminology (A, B, C axis?) is confusing.Not understanding the axis can make choosing the right machine or process feel overwhelming, potentially limiting your projects or leading to costly mistakes.Let’s break down what those 5 axis are in simple terms, so you know exactly what capabilities they offer.
A 5-axis CNC machining center typically moves a tool or workpiece along three linear axis (X, Y, and Z – like up/down, left/right, forward/back) and rotates on two additional rotary axis (often A and B, rotating around the X and Y axis respectively). This allows machining from multiple angles in a single setup.
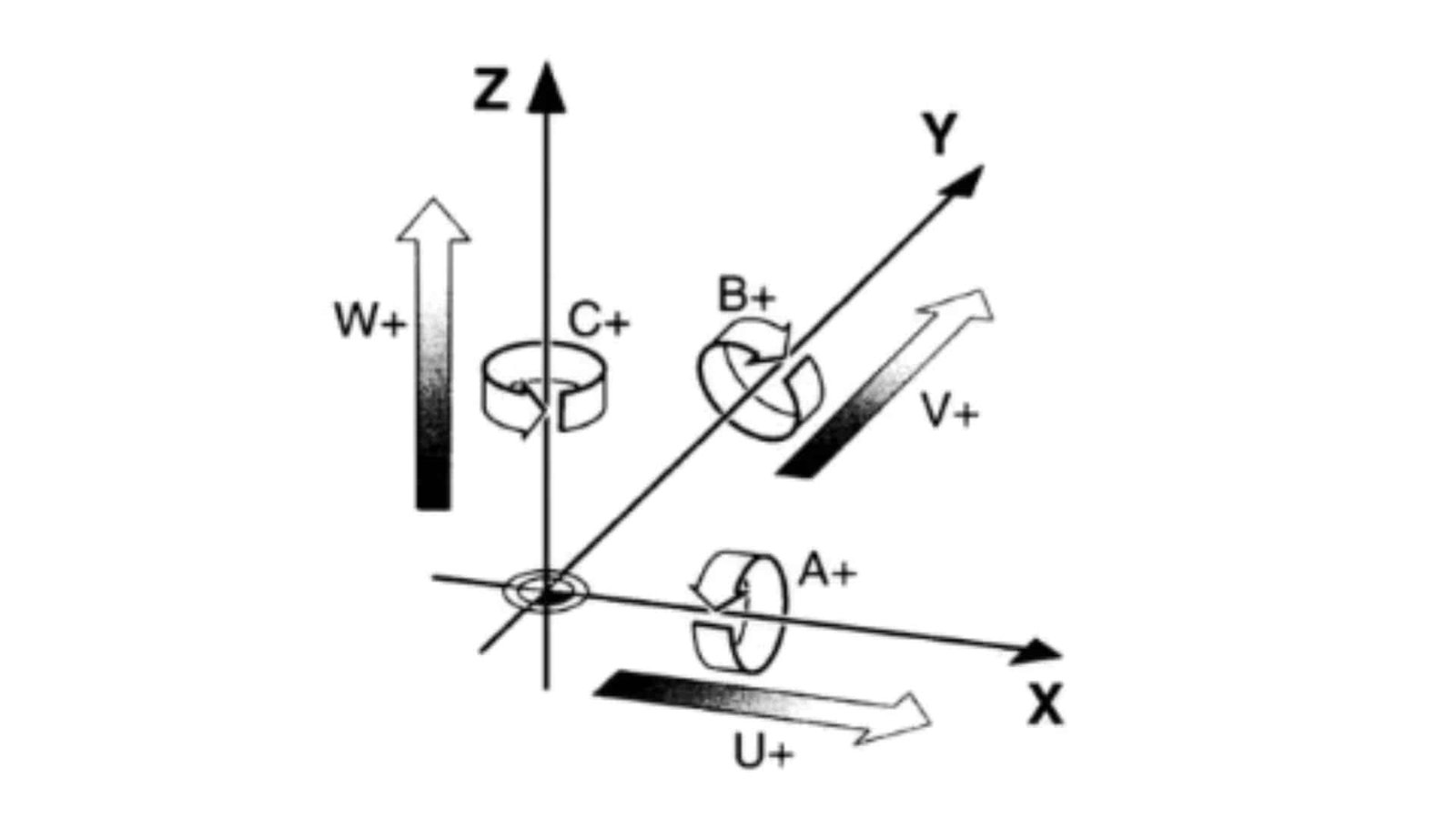
Understanding these movements is the key to unlocking advanced machining possibilities. Let’s also explore related concepts like 3+2 machining and see how these different setups compare.
What are the 3+2 Machining Technology on a CNC Machining Center?
You’ve encountered terms like "3+2 machining," "positional 5-axis," or "indexed 5-axis." How is this different from a "true" or "simultaneous" 5-axis machine?Choosing between 3+2 and full 5-axis without understanding the distinction could mean buying more capability than you need, or not having the capability for complex jobs.Let’s clarify what 3+2 machining involves, its benefits, and where it fits within the CNC machining world.
3+2 machining uses a 5-axis machine, but the two rotary axis (the 4th and 5th axis) lock the tool or workpiece into a specific tilted position. Then, the machine performs the cutting using only the three linear axis (X, Y, Z), essentially like a 3-axis machine working at an angle.

Think of 3+2 machining1 (also called positional or indexed 5-axis) as a smart way to use a 5-axis machine for parts that don’t need all axis moving at once. The machine uses its rotary axis (like A rotating around X, B rotating around Y) to tilt the workpiece or the tool head to a desired angle. Once set, these rotary axis are locked. Then, the actual cutting happens using only the standard X, Y, and Z movements. The key difference from simultaneous 5-axis is that the rotary axis do not move during the cut. This approach offers several advantages:
- Shorter, more rigid tools: Better tool access at an angle allows using shorter tools2, reducing vibration and improving surface finish.
- Better Access: The spindle head can reach areas on the workpiece that would be difficult or impossible with a purely vertical 3-axis setup.
- Reduced Setups: You can machine multiple faces of a part in a single clamping, improving accuracy (less re-fixturing error) and saving time compared to using a 3-axis machine for the same job.
- Cost-Effective: It provides multi-sided machining capabilities without the full complexity and cost of simultaneous 5-axis programming and control. It’s great for parts with multiple flat faces at different angles.
What are the differences 3 axis, 5 axis and 3+2 machining technology cnc machining center?
3-axis, 3+2, simultaneous 5-axis… it’s easy to get tangled in the terminology. What truly sets them apart in practical terms?If you don’t grasp the core differences in capability and application, you might invest in the wrong technology, hindering your shop’s potential or overspending.Let’s clearly outline the distinctions between these three common CNC machining approaches based on how they move and what they can achieve.
The main difference lies in how the axis move during cutting. 3-axis moves only X, Y, Z. 3+2 fixes the angle using two rotary axis then cuts using X, Y, Z. True (simultaneous) 5-axis can move all five axis (X, Y, Z, and two rotary) together during the cut.

Let’s compare the capabilities:
- 3-Axis Machining3: This is the foundation. The tool moves linearly along X, Y, and Z. It’s best for parts with simple geometry, like drilling holes on a flat plate, facing surfaces, or cutting 2D/2.5D profiles. It struggles with undercuts or deep, narrow cavities and often requires manually repositioning the part (multiple setups) for machining different faces, increasing labor and potential errors.
- 3+2 Axis Machining (Positioning/Indexed): This acts as a bridge. It uses the 5-axis machine’s rotary axis to orient the part, then locks them and performs 3-axis cutting. Its strength is efficiently machining multiple faces or angled features on a part in a single setup. It’s ideal for parts with multiple flat surfaces at compound angles, reducing setup time and improving accuracy over multiple 3-axis setups. It’s a practical, cost-effective middle ground.
- 5-Axis Simultaneous Machining4: This is the most advanced. All five axis can move concurrently during the cut, allowing the tool to follow complex contours smoothly. This is essential for true 3D surface machining, creating shapes like turbine blades, impellers, medical implants, or complex molds with flowing surfaces and undercuts. It offers the highest flexibility and enables single-setup machining for very complex parts, crucial in aerospace and medical fields.
| Aspect | 3-Axis | 3+2 Axis (Positioning) | 5-Axis Simultaneous |
|---|---|---|---|
| axis Used | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z (A, B fixed during cut) | X, Y, Z, A, B (all moving) |
| Movement | Linear only | Position A, B; then linear X, Y, Z | Simultaneous linear & rotary |
| Part Complexity | Simple geometries, flat | Multi-sided, angled flat features | Complex curves, undercuts |
| Setup Needs | Multiple setups often needed | Fewer setups than 3-axis | Single setup often possible |
| Programming | Simplest | Moderate complexity | Most complex |
| Operator Skill | Basic | Moderate | Advanced |
| Cost | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
| Applications | Simple parts, high volume | Parts with multiple angled faces | Aerospace, medical, molds |
An unexpected detail for some is realizing that 3+2 isn’t just a limited 5-axis, but a distinct strategy that cleverly bridges the gap between 3-axis simplicity and full 5-axis complexity.
How to choose from the 3 axis, 5 axis and 3+2 machining technology cnc machining center?
Now you understand the differences, but the critical question remains: which technology is the right investment for your specific work and business?
Making the wrong choice is expensive – either you pay for capabilities you rarely use, or you lack the ability to take on profitable, complex jobs, limiting growth.
Let’s examine the key factors to consider when deciding between 3-axis, 3+2, and simultaneous 5-axis machines for your shop.
The best choice depends heavily on the complexity of the parts you make, required accuracy, production volume, and your budget. Simple parts suit 3-axis, multi-sided parts suit 3+2, and highly complex curved shapes demand true 5-axis.

Choosing the right machine requires balancing capability with operational realities. Consider these crucial points:
- Part Complexity and Geometry: This is paramount. If your work is mostly simple, prismatic parts machined from one or two sides, a 3-axis machine is likely the most efficient and cost-effective. If parts require features on multiple faces or at compound angles (but are mostly planar on those faces), 3+2 machining offers significant advantages in reducing setups and improving accuracy. If you need to produce parts with true complex curves, undercuts, and flowing surfaces (molds, impellers, aerospace components, medical implants), then simultaneous 5-axis capability is essential.
- Production Volume and Cost: For high-volume production of simple parts, 3-axis machines usually offer the lowest cost per part and are simpler to operate. For low-volume, high-complexity parts, the setup time savings and single-setup capability of 5-axis (or 3+2) can make it more efficient overall, despite the higher machine cost. 3+2 provides a good balance for medium complexity and volume.
- Budget and Operator Skill: Machine costs increase significantly from 3-axis to 3+2 to simultaneous 5-axis. Furthermore, programming and operating complexity also increase. 5-axis simultaneous work requires advanced CAM software and highly skilled programmers and operators. Factor in the costs of the machine, software, and training.
- Accuracy Requirements: Both 3+2 and 5-axis generally offer better accuracy for multi-sided parts compared to multiple setups on a 3-axis machine, simply by eliminating re-clamping errors. For the absolute highest accuracy on complex contours, 5-axis simultaneous is typically superior.
- Floor Space and Maintenance: More complex machines like 5-axis centers can be larger and potentially have higher maintenance requirements than simpler 3-axis machines. Consider your available shop space and maintenance resources.
Analyze the majority of your current and anticipated work. Don’t invest in 5-axis if 95% of your jobs are simple 3-axis work. Conversely, if complex parts are your target market, investing in 3+2 or 5-axis capability could be crucial for growth.
Conclusion
Choosing between 3-axis, 3+2, and simultaneous 5-axis CNC machining centers requires understanding their core differences in movement and capability. Aligning the technology with your specific part complexity, production needs, budget, and skill level ensures you make the most effective investment for your machining operations.
-
Explore this link to understand how 3+2 machining enhances efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of using shorter tools in machining, including reduced vibration and improved surface finish. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the pros and cons of 3-Axis Machining, which is essential for basic machining tasks. ↩
-
Discover the applications and benefits of 5-Axis Simultaneous Machining, crucial for advanced manufacturing in aerospace and medical fields. ↩
